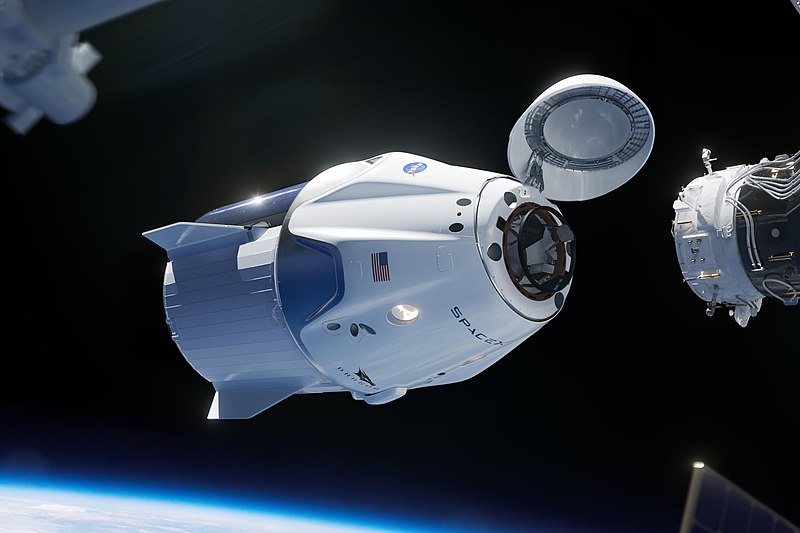
The space tourism of Richard Branson, Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos could undo the progress made to heal the ozone layer, scientists have said.
New research has probed the impact of craft leaving and returning to Earth on the atmosphere - in particular the upper parts, Skynews reports.
A combined study by UCL, the University of Cambridge and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology found the soot given off by spacecraft was damaging the layer of protective ozone around the planet - and retains heat at 500 times the rate of other soot sources.
Study co-author Dr Eloise Marais of UCL said likening spacecraft emissions with aircraft and ground-based sources was therefore "erroneous".
While scientists found the current damage is small, they suggested regulation on the growing industry of people travelling to space for touristic purposes to protect from future problems.
What is the ozone layer?
The ozone layer is a part of the atmosphere made up of O3 oxygen molecules - as opposed to the O2 oxygen that is more commonly found in the air.
It protects the surface of the earth from vast amounts of ultraviolet radiation sent out by the Sun, which if let through could cause temperatures to rise.
Scientists campaigned from the 1970s for rule changes after noticing the layer was getting depleted.
It was established that certain chemicals were causing the damage, and in 1987 the Montreal Protocol was introduced to ban the substances - it is the only UN treaty ever ratified by all 198 member states.
The holes in the ozone layer have since started to be repaired - although mostly at higher altitudes.
The damage from space travel
The scientists studying space travel examined data from 103 rocket launches in 2019, and also trips by Branson's Virgin Galactic, Mr Musk's SpaceX and Mr Bezos's Blue Origin spacecraft.
They found the warming due to soot more than doubled after just three years of additional emissions from space tourism, due to added rubber in the fuel, among other reasons.
The fact the soot is expelled in the upper atmosphere increases the damage - the particles being 500 times more efficient at retaining heat than other soot.
If space tourism was to go ahead with weekly trips, it would undermine the success of the Montreal Protocol, the research said.
The study's lead author, Dr Robert Ryan of UCL, said: "The only part of the atmosphere showing strong ozone recovery post-Montreal Protocol is the upper stratosphere, and that is exactly where the impact of rocket emissions will hit hardest.
"We weren't expecting to see ozone changes of this magnitude, threatening the progress of ozone recovery."
The findings were published in the Earth's Future journal.